If a government (outside monetary unions) can make a draft at the central bank, why do rating agencies rate governments’ creditworthiness?
In this post, I will attempt to describe the dynamics of defaults and restructurings by going through some monetary economics of open economies.
Carmen Reinhart and Kenneth Rogoff wrote a book in 2009 titled This Time Is Different: Eight Centuries Of Financial Folly or simply This Time Is Different arguing that governments do indeed default – both in debt denominated in the domestic and foreign currencies. They blame the public debt and the government for the public debt – hence giving the innuendo that governments across the planet should attempt to cut public debt by tight fiscal policies. This is an illegitimate conclusion – on which I will say more below.
At another extreme are the Chartalists who argue that the government cannot “run out of money” and hence fiscal policy has no monetary constraints. Sometimes they qualify this statement by saying that the currency they are discussing are “sovereign currencies”. Now, there are various definitions of what a sovereign currency is but it is frequently pointed out by them that nations who have seen restructuring of government debt did not have a “sovereign currency” – because the currency is either pegged or fixed or it is the case that the government had a lot of debt in foreign currency which presumably allows defaults/restructuring of government debt in the domestic currency as well. The motivation behind this is Milton Friedman’s idea that nations should freely float their currencies in international markets and that markets will clear and that the State intervention in the currency markets can only make things worse. Hence Reinhart/Rogoff don’t prove them wrong – according to them – since the situations are supposedly different.
We will see that while there is some truth to it, the notion of a “sovereign currency” is highly misleading. Such intuitions are coincident with the incorrect notion that indebtedness to foreigners (in domestic currency) is just a technical liability and there’s nothing more to that!
Here’s S&P’s article on the methodology it uses to assign ratings on governments: Standard & Poor’s – Sovereign Government Rating And Methodology. One can see the importance it gives to the external sector. However, S&P does not provide a mechanism on how a government will finally end up defaulting. The purpose of this post is to look into this.
Before this let us make a connection between the public debt and the net indebtedness of a nation. Most people in the planet confuse the two. The former is the debt of the government whereas the latter is the (net) indebtedness of the nation as a whole. This is the net international investment position (adjusting for traditional settlement assets such as gold) with the sign reversed. This can be obtained by consolidating all the sectors of an economy and the consolidation involves (for example) netting of the assets of the domestic private sector held abroad and also its gross indebtedness to the rest of the world.
So one can think of two extremes:
- Japan – with a high public debt of about 195% of gdp (includes just the central government debt), while being a net creditor of the world. It’s NIIP is about 50% of gdp (data source: MoF, Japan)
- Australia – with a low public debt of 18% of gdp and NIIP of minus 59% of gdp.
So in the case of Japan, while the government is a huge debtor, the nation as a whole is a creditor, whereas in the case of Australia, it is the opposite. So the rating agencies get it wrong or opposite!
Let us first assume a closed economy. The greatest starting point in analyzing economies is the sectoral balances approach. For a closed economy it is:
NAFA = DEF
where NAFA is the Net Accumulation of Financial Assets of the private sector and DEF is the government’s budget deficit. If the private sector wants to accumulate a lot of financial assets, and the government wants to run the economy near full employment, the public debt will be higher, the higher the propensity to save, for example. (This is not as straightforward as presented here but can be shown in a simple stock-flow consistent model). So unlike what neoclassical economists think, the level of public debt is somewhat irrelevant. Neither does the government has too much trouble in financing its debt because the public debt is the mirror image of the private sector net financial asset position.
Now let us take the case of an open economy. The sectoral balances identity now is
NAFA = DEF + CAB
A deficit in the current account implies an increase in the net indebtedness to foreigners. Unless the markets miraculously clear with the exchange rate adjusting to bring the CAB in balance, a deficit in the current account implies the nation as a whole has to attract foreigners to finance this deficit i.e., via a lower NAFA or higher DEF. In the long run, the private sector is accumulating financial assets (or has small positive NAFA) and the whole of the current account balance is reflected in the public sector balance.
So the debate fixed vs floating doesn’t help too much. A relaxation of fiscal policy may spill over into higher imports with the public debt and the net indebtedness to foreigners keeps rising forever to gdp. Hence nations typically have to curb growth to bring the current account into balance.
An excellent reference for this is New Cambridge Macroeconomics And Global Monetarism – Some Issues In The Conduct Of U.K. Economic Policy, 1978, by Martin Fetherston and Wynne Godley.
This is theory. So let’s look at an open economy mechanism of an event of default by the government as a story.
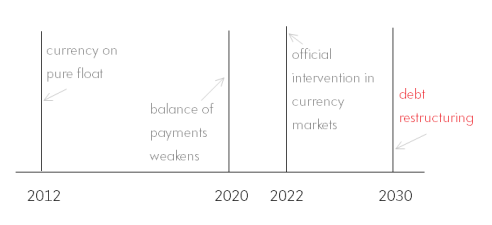
In the following, I will use the phrase “pure float” instead of the dubious terminology “sovereign currency”.
Here’s the simplest model:
In the above, a nation with its currency on a pure float and with zero official sector liabilities in foreign currencies has a somewhat weak external position in 2012. Now, according to some of the Neochartalist arguments this nation can’t default on its government debt. However this is a wrong conclusion as the scenario above hightlights. In the scenario constructed, the balance of payments position weakens over the years (and I have mentioned that roughly in 2020 it weakens). In 2022, foreigners are no longer willing to finance the debt. This may be due to a capital flight or due to the inability of the banking system to maintain a low net open position in foreign currency. The depreciation of the domestic currency isn’t sufficient to clear the fx markets and the official sector (either the central bank or the government’s treasury) necessarily has to intervene in the foreign exchange markets by issuing debt denominated in foreign currency. The government is then acting as the borrower of the last resort and the objective is to use the proceeds to partially have more foreign exchange reserves and/or to sell the foreign currency proceeds from the debt issuance to clear the fx markets. The government is then left with a net liability position in the foreign currency. Soon the external situation worsens to the point requiring official foreign help – such as from the IMF – which promises to help and requires a restructuring of the debt both in domestic and foreign currencies.
Free marketers have a blind belief in the markets and the theories are built on the assumption that markets always clear. The recent crisis has highlighted that this isn’t the case. Even for the case of Australia – whose currency can be considered closed to being pure float – has had issues in the external sector and the Reserve Bank of Australia had to borrow in US dollars from the Federal Reserve (via swap lines) to help Australian banks meet their foreign currency funding needs during the crisis.
Of course the above is not typical but to prevent the external vulnerability to go out of control, governments keep domestic demand low and a lot of times, they over-do this.
The point of the exercise is to prove that it is not meaningless to think of nations becoming bankrupt in whichever situation one can think of and it doesn’t help to laugh at the rating agencies and make fun of them – possibly with the exception for the case of Japan. Statements such as “government with a sovereign currency cannot become bankrupt” are simply misleading. In the above, the Chartalists would argue that the currency was not sovereign and they were not wrong about the default but the currency was sovereign in their own definition in 2012!
Here are some comments on some nations.
Japan: As mentioned above, Japan is a net creditor of the rest of the world and partially as a consequence of that, most of the Japanese government’s debt is held internally. The rating agencies are aware of this but in spite of this continue to make comments on the creditworthiness of the Japanese government. It is possible that residents may transfer funds abroad for unknown reasons (which the raters for some reason suspect) but it may require just a minor interest rate hike to prevent this from happening. Japan has a relatively strong external situation and hence has no issues in financing its government debt.
Canada: Nick Rowe of WCI mentioned to me on his blog that worrying about the balance of payments constraint is like “beating a dead horse” – citing the example of Canada which has floated its currency and it seems has no trouble with its external sector. But this ignores other things in the formulation of the problem. Canada is an advanced nation and an external situation which is not weak. However, a growth of the nation much faster than the rest of the world will lead to a worsening of the external situation. To some extent the nation’s external situation has been the result of its relatively better competitiveness of exporters compared to its propensity to import and a demand situation which either as a conscious attempt of demand management of the government or by pure fluke has helped its external situation remain non-vulnerable.
United States: The US dollar is the reserve currency of the world and slowly over time, the United States has turned from being a creditor of the rest of the world to becoming the world’s largest debtor nation. (Again not due to its public debt but because of its net indebtedness to foreigners). The US external sector is a great imbalance and any attempt to get out of the recession by fiscal policy alone will worsen its external situation leading to a crash at some point. S&P is right! So to come out of the depressed state, the nation has to complement fiscal expansion with improvement of the external situation such as by (and not restricted to) asking trading partners to not revalue their currencies. Still for some reasons bloggers at the “New Economic Perspectives” think that
… Bernanke also knows that the US has infinite ability to finance these fiscal components, that there is no solvency issue and that the policy rate and both ends of the yield curve are under the direct control of the Fed.
Back to This Time Is Different. While Reinhart and Rogoff’s analysis of government debt may be useful, their conclusions can be destructive for the world as a whole. The domestic private sector of a nation needs continuous injection from outside so that it can run surpluses in general and tightening of fiscal policies will lead to a depression. Global imbalances is crucial in understanding the nature of this crisis (and not public debt alone) and even coordinated attempts to reflate economies may provide only a temporary relief. Since failure in international trade restricts the growth of nations and their attempts to reach full employment, what the world needs is an entirely different way to run the economies under managed trade with fiscal expansion. Ideas of “free trade” such as that outlined here by Alan Blinder simply help some classes of society at the expense of others because it relies on the “market mechanism” which has failed over and over again.
This brings me to “sovereignty”. As argued, the concept “sovereign currency” is almost vacuous (except highlighting the problems of the Euro Area) but sovereignty as argued by Wynne Godley in his great 1992 article Maastricht And All That and by Anthony Thirlwall in the same year on FT (my post on it here Martin Wolf Pays A Generous Tribute To Anthony Thirlwall) definitely have great importance. Some of Thirwall’s concepts of economic sovereignty in the article were: the ability to protect and encourage strategic industries, the possibility of designing systems of managed trade to even out payments imbalances, the ability to protect against certain countries with persistent surpluses, differential taxes which discriminate in favour of the tradeable goods sector.